What happens on day 4 without cdk?
Day 4 without cdk is a critical juncture in the cell cycle, marking the point at which cells lacking cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) activity undergo apoptosis, or programmed cell death.
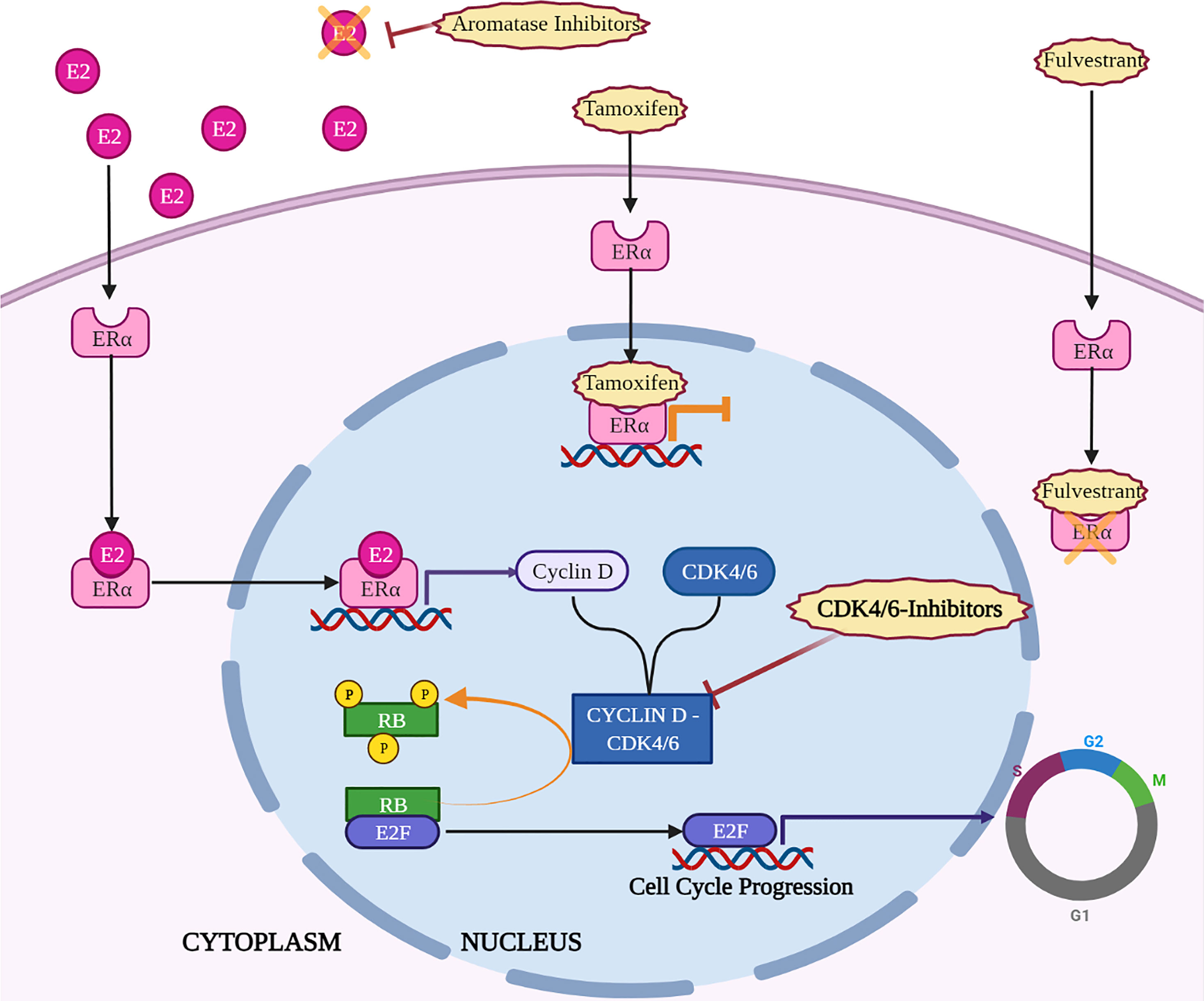
CDK is a key regulator of the cell cycle, and its inhibition leads to a cascade of events that ultimately result in cell death. One of the most important roles of CDK is to phosphorylate retinoblastoma protein (Rb), which releases E2F transcription factors and allows them to promote the expression of genes required for cell cycle progression. Without CDK activity, Rb remains hypophosphorylated and E2F is sequestered, leading to cell cycle arrest. In addition, CDK inhibition also leads to the activation of p53, a tumor suppressor protein that induces apoptosis.
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To Rara Nadifa Unlocking Her Secrets For Success
The importance of day 4 without cdk is underscored by the fact that it represents a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment. By inhibiting CDK activity, it may be possible to induce apoptosis in cancer cells and prevent their proliferation.
CDK and Cell Cycle Regulation
Introduction: CDK is a key regulator of the cell cycle, and its inhibition leads to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.Facets: CDK phosphorylates Rb, releasing E2F transcription factors and allowing them to promote the expression of genes required for cell cycle progression.CDK inhibition also leads to the activation of p53, a tumor suppressor protein that induces apoptosis.Summary: CDK activity is essential for cell cycle progression, and its inhibition can lead to cell death.Day 4 without CDK and Cancer Treatment
Introduction: Day 4 without CDK represents a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment.Further Analysis: By inhibiting CDK activity, it may be possible to induce apoptosis in cancer cells and prevent their proliferation.Summary: CDK inhibition is a promising strategy for the treatment of cancer.Day 4 without CDK
Day 4 without CDK is a critical juncture in the cell cycle, marking the point at which cells lacking cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) activity undergo apoptosis, or programmed cell death.
- CDK inhibition: This leads to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
- Rb phosphorylation: CDK phosphorylates Rb, releasing E2F transcription factors and allowing them to promote cell cycle progression.
- p53 activation: CDK inhibition also leads to the activation of p53, a tumor suppressor protein that induces apoptosis.
- Cell cycle regulation: CDK is a key regulator of the cell cycle.
- Cancer treatment: Day 4 without CDK represents a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment.
These aspects highlight the importance of CDK in cell cycle regulation and its potential role in cancer treatment. By understanding the mechanisms of CDK inhibition, it may be possible to develop new therapies for cancer and other diseases.
CDK inhibition
CDK inhibition is a critical event in the process of day 4 without CDK. CDK is a key regulator of the cell cycle, and its inhibition leads to a cascade of events that ultimately result in cell death. One of the most important roles of CDK is to phosphorylate retinoblastoma protein (Rb), which releases E2F transcription factors and allows them to promote the expression of genes required for cell cycle progression. Without CDK activity, Rb remains hypophosphorylated and E2F is sequestered, leading to cell cycle arrest.
In addition, CDK inhibition also leads to the activation of p53, a tumor suppressor protein that induces apoptosis. p53 is activated in response to a variety of cellular stresses, including DNA damage, oncogene activation, and hypoxia. Once activated, p53 can trigger apoptosis by a number of mechanisms, including the induction of pro-apoptotic genes and the inhibition of anti-apoptotic genes.
The connection between CDK inhibition and day 4 without CDK is therefore clear. CDK inhibition is a key event in the process of day 4 without CDK, and it leads to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To Understanding Blue Face From Wife
This understanding has important implications for cancer treatment. By inhibiting CDK activity, it may be possible to induce apoptosis in cancer cells and prevent their proliferation. This is a promising strategy for the treatment of cancer, and it is currently being investigated in clinical trials.
Rb phosphorylation
Rb phosphorylation is a critical step in the cell cycle, and its inhibition is a key event in the process of day 4 without CDK. CDK phosphorylates Rb, releasing E2F transcription factors and allowing them to promote the expression of genes required for cell cycle progression. Without CDK activity, Rb remains hypophosphorylated and E2F is sequestered, leading to cell cycle arrest.
- Role of Rb phosphorylation
Rb phosphorylation is essential for the G1/S transition of the cell cycle. By phosphorylating Rb, CDK releases E2F transcription factors, which then promote the expression of genes required for DNA replication and cell division.
- Consequences of Rb phosphorylation inhibition
Inhibition of Rb phosphorylation leads to cell cycle arrest. This is because hypophosphorylated Rb sequesters E2F transcription factors, preventing them from promoting the expression of genes required for cell cycle progression.
- Implications for day 4 without CDK
On day 4 without CDK, Rb phosphorylation is inhibited, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. This is a critical event in the process of day 4 without CDK, and it represents a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment.
By understanding the role of Rb phosphorylation in the cell cycle, and its inhibition on day 4 without CDK, it is possible to develop new therapies for cancer and other diseases.
p53 activation
The activation of p53 is a critical event in the process of day 4 without CDK. p53 is a tumor suppressor protein that is activated in response to a variety of cellular stresses, including DNA damage, oncogene activation, and hypoxia. Once activated, p53 can trigger apoptosis by a number of mechanisms, including the induction of pro-apoptotic genes and the inhibition of anti-apoptotic genes.
CDK inhibition leads to the activation of p53 by a number of mechanisms. One mechanism is through the inhibition of MDM2, a negative regulator of p53. MDM2 binds to p53 and targets it for degradation. By inhibiting CDK, MDM2 is phosphorylated and inactivated, leading to the stabilization and activation of p53.
Another mechanism by which CDK inhibition leads to the activation of p53 is through the induction of DNA damage. CDK is required for the proper replication of DNA. By inhibiting CDK, DNA replication is impaired, leading to DNA damage. DNA damage is a potent activator of p53.
The activation of p53 on day 4 without CDK is a critical event that leads to apoptosis. This understanding has important implications for cancer treatment. By inhibiting CDK activity, it may be possible to induce apoptosis in cancer cells and prevent their proliferation. This is a promising strategy for the treatment of cancer, and it is currently being investigated in clinical trials.
In summary, the activation of p53 is a critical component of day 4 without CDK. CDK inhibition leads to the activation of p53 by a number of mechanisms, including the inhibition of MDM2 and the induction of DNA damage. The activation of p53 leads to apoptosis, which is a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment.
Cell cycle regulation
The cell cycle is a complex and tightly regulated process that ensures the accurate duplication and segregation of genetic material. CDK is a key regulator of the cell cycle, and its inhibition leads to a cascade of events that ultimately result in cell death.
- CDK and cell cycle progression
CDK is required for the proper progression of the cell cycle. It phosphorylates a number of proteins that are involved in cell cycle regulation, including Rb and p53. By phosphorylating these proteins, CDK promotes their activation and allows them to carry out their functions.
- CDK inhibition and cell cycle arrest
The inhibition of CDK leads to cell cycle arrest. This is because CDK is required for the phosphorylation of Rb and p53, two proteins that are essential for cell cycle progression. Without CDK activity, Rb remains hypophosphorylated and p53 is not activated, leading to cell cycle arrest.
- CDK inhibition and apoptosis
In addition to cell cycle arrest, CDK inhibition also leads to apoptosis. This is because the inhibition of CDK leads to the activation of p53, a tumor suppressor protein that induces apoptosis. p53 is activated in response to a variety of cellular stresses, including DNA damage, oncogene activation, and hypoxia. Once activated, p53 can trigger apoptosis by a number of mechanisms, including the induction of pro-apoptotic genes and the inhibition of anti-apoptotic genes.
The connection between cell cycle regulation and day 4 without CDK is therefore clear. CDK is a key regulator of the cell cycle, and its inhibition leads to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. This understanding has important implications for cancer treatment. By inhibiting CDK activity, it may be possible to induce apoptosis in cancer cells and prevent their proliferation. This is a promising strategy for the treatment of cancer, and it is currently being investigated in clinical trials.
Cancer treatment
The connection between cancer treatment and day 4 without CDK lies in the critical role of CDK in cell cycle regulation and its inhibition as a potential therapeutic strategy for cancer.
- CDK inhibition and cell cycle arrest
CDK inhibition leads to cell cycle arrest, preventing the uncontrolled proliferation of cancer cells. By blocking CDK activity, it is possible to halt the cell cycle and induce apoptosis, or programmed cell death, in cancer cells.
- CDK inhibition and apoptosis
CDK inhibition also triggers apoptosis in cancer cells. The inhibition of CDK leads to the activation of p53, a tumor suppressor protein that promotes apoptosis. p53 can induce apoptosis through various mechanisms, including the activation of pro-apoptotic genes and the inhibition of anti-apoptotic genes.
- CDK inhibitors in cancer treatment
Given the role of CDK in cell cycle regulation and apoptosis, CDK inhibitors have emerged as promising therapeutic agents for cancer treatment. Several CDK inhibitors have been developed and are currently being evaluated in clinical trials for the treatment of various types of cancer.
- Challenges in CDK inhibition
While CDK inhibition holds promise for cancer treatment, there are also challenges to overcome. One challenge is the potential for CDK inhibitors to cause side effects, as CDK is involved in various cellular processes. Another challenge is the development of resistance to CDK inhibitors, which can limit their long-term effectiveness.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of CDK inhibition for cancer treatment are significant. By targeting CDK and inducing apoptosis in cancer cells, it may be possible to improve outcomes for patients with cancer.
FAQs on "Day 4 without CDK"
This section addresses frequently asked questions about "day 4 without CDK," providing concise and informative answers to enhance understanding of the topic.
Question 1: What is the significance of day 4 without CDK?
Day 4 without CDK marks a critical juncture in the cell cycle where cells lacking cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) activity undergo apoptosis, or programmed cell death. CDK is a key regulator of the cell cycle, and its inhibition leads to a cascade of events that ultimately result in cell death.
Question 2: How does CDK inhibition contribute to cancer treatment?
CDK inhibition represents a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment. By inhibiting CDK activity, it may be possible to induce apoptosis in cancer cells and prevent their uncontrolled proliferation. CDK inhibitors are currently being evaluated in clinical trials for the treatment of various types of cancer.
Summary: Understanding the significance of day 4 without CDK and the role of CDK inhibition in cancer treatment provides valuable insights for researchers and healthcare professionals working towards the development of effective cancer therapies.
Conclusion
In summary, "day 4 without CDK" marks a critical juncture in the cell cycle, where cells lacking cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) activity undergo apoptosis. CDK inhibition has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment, as it can induce apoptosis in cancer cells and prevent their uncontrolled proliferation. Understanding the mechanisms underlying day 4 without CDK and the role of CDK inhibition provides valuable insights for researchers and healthcare professionals working towards the development of effective cancer therapies.
As research continues to shed light on the complexities of cell cycle regulation and cncer biology, the significance of day 4 without CDK and the potential of CDK inhibition as a therapeutic target will undoubtedly continue to be explored and refined. This ongoing pursuit of knowledge holds great promise for the advancement of cancer treatment and improved outcomes for patients.