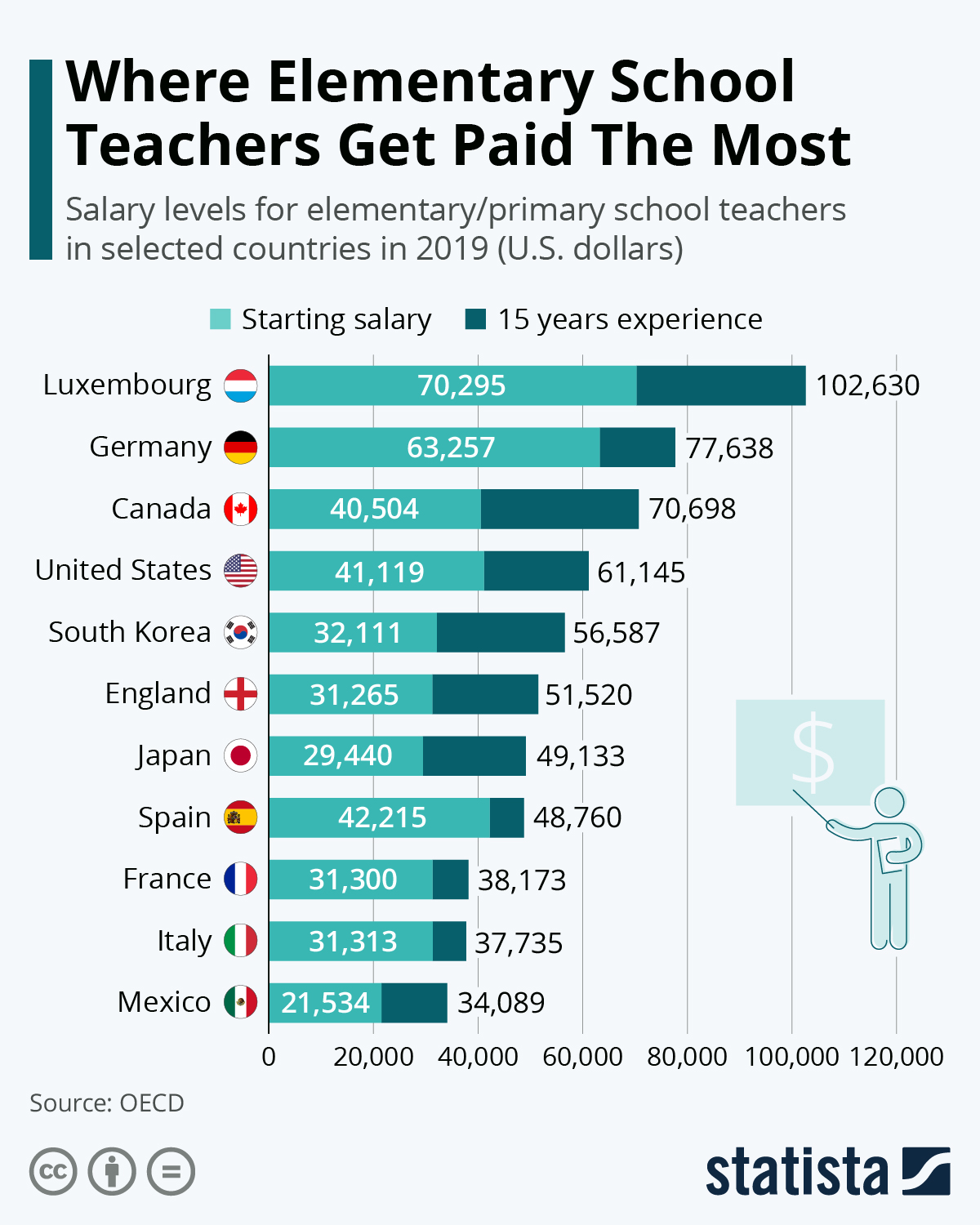
Teaching is one of the most vital professions in society, shaping the future by educating and inspiring young minds. Yet, many people wonder how much teachers get paid and whether their compensation reflects the immense responsibility they shoulder. While teacher salaries vary significantly depending on location, experience, and subject matter, understanding the broader picture can help shed light on this critical issue. Teachers not only impart knowledge but also contribute to the social and emotional development of their students. Despite their essential role, questions about their pay often arise, with debates focusing on whether educators are fairly compensated for their efforts. This article delves into the factors that influence teacher salaries and provides a comprehensive overview of how much teachers get paid across different contexts.
In recent years, discussions about teacher pay have gained momentum, especially as education systems face challenges like teacher shortages and burnout. The average salary of a teacher depends on multiple factors, including the level of education they provide, the state or country they work in, and their years of experience. While some regions offer competitive salaries and robust benefits, others struggle to attract and retain qualified educators due to lower pay scales. This disparity raises important questions about how much teachers get paid and whether current compensation models are sustainable.
Furthermore, understanding teacher pay involves looking beyond the base salary. Benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off also play a significant role in determining the overall value of a teaching position. By examining these components, we can gain a clearer picture of how much teachers get paid and what influences their financial well-being. In this article, we will explore various aspects of teacher compensation, including regional variations, career progression, and the impact of policy changes, to provide a holistic view of this critical topic.
Read also:Jack Harlow And Diddy A Dynamic Duo Shaping The Music Industry
Table of Contents
- What Factors Influence How Much Teachers Get Paid?
- How Does Geography Affect Teacher Salaries?
- Why Do Some Teachers Earn More Than Others?
- What Are the Benefits Beyond the Salary?
- Is Teaching a Lucrative Career Choice?
- How Can Teachers Increase Their Earning Potential?
- What Role Do Policies Play in Teacher Compensation?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Teacher Pay
What Factors Influence How Much Teachers Get Paid?
Several key factors determine how much teachers get paid, and understanding these elements is crucial for gaining insight into teacher compensation. One of the most significant factors is the level of education they provide. For example, elementary school teachers often earn less than high school or college-level educators due to differences in curriculum complexity and student needs. Additionally, teachers who specialize in high-demand subjects like mathematics, science, or special education may receive higher salaries to reflect the scarcity of qualified professionals in these areas.
Experience also plays a pivotal role in determining teacher pay. New teachers typically start at the lower end of the salary scale, with incremental raises as they gain tenure and demonstrate effectiveness in the classroom. School districts often have structured pay scales that reward educators for years of service, advanced degrees, or additional certifications. These factors contribute to a teacher's earning potential and help explain why some educators earn significantly more than others, even within the same district.
Another important consideration is the funding available to schools. Public schools rely heavily on local, state, and federal funding, which directly impacts teacher salaries. Schools in affluent areas may have more resources to allocate toward competitive salaries, while those in underfunded districts may struggle to offer comparable pay. Understanding these dynamics is essential for grasping the broader context of how much teachers get paid and why disparities exist across regions.
How Does Geography Affect Teacher Salaries?
Geography is one of the most influential factors affecting how much teachers get paid. Salaries can vary dramatically depending on the state, city, or even school district where an educator works. For instance, teachers in states like New York and California tend to earn higher salaries compared to those in states like Mississippi or Oklahoma. This discrepancy is often attributed to differences in the cost of living, with higher-paying states typically having a higher cost of living as well.
Urban vs. Rural Pay Gaps
Within states, urban and rural areas also exhibit significant differences in teacher pay. Urban districts often have larger budgets and can afford to offer higher salaries to attract top talent. In contrast, rural schools may struggle to compete, leading to lower pay scales and difficulty retaining experienced educators. This urban-rural divide highlights the challenges faced by teachers in less populated areas and underscores the importance of addressing regional disparities.
Regional Variations in Benefits
Beyond base salaries, regional variations in benefits also impact how much teachers get paid. Some states offer robust retirement plans and healthcare packages, while others provide minimal support. For example, teachers in states with strong teachers' unions often benefit from better collective bargaining agreements, which can lead to higher overall compensation. Understanding these regional nuances is essential for evaluating teacher pay holistically.
Read also:Blackrocks Strike Against Trump Exposing The Shorting Of A Former Presidents Investments
Why Do Some Teachers Earn More Than Others?
While the teaching profession is often perceived as having uniform pay structures, the reality is that some teachers earn significantly more than their peers. This disparity can be attributed to a combination of factors, including specialization, advanced degrees, and leadership roles. For instance, teachers who hold master's degrees or doctoral qualifications often receive higher salaries, as their advanced education is seen as an asset to the school system.
Specialization and Subject Matter
Teachers who specialize in high-demand subjects like STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) or special education frequently command higher salaries. This is because these fields often face shortages of qualified educators, prompting schools to offer competitive pay to attract and retain talent. Additionally, teachers who take on extracurricular responsibilities, such as coaching or leading after-school programs, may receive stipends that boost their overall earnings.
Leadership and Administrative Roles
Another way teachers can increase their earning potential is by taking on leadership roles within their schools. Positions such as department head, curriculum coordinator, or assistant principal often come with higher pay grades. These roles require additional responsibilities and expertise, making them a natural progression for experienced educators seeking to advance their careers. By exploring these opportunities, teachers can significantly impact how much they get paid over time.
What Are the Benefits Beyond the Salary?
When evaluating how much teachers get paid, it's essential to consider the benefits that come with the job. While base salaries are a critical component of compensation, benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off can significantly enhance a teacher's overall financial well-being. For many educators, these perks make teaching a more attractive career choice despite the challenges they face in the classroom.
Healthcare and Retirement Packages
Teachers often receive comprehensive healthcare coverage, including medical, dental, and vision insurance, which can be a substantial financial advantage. Additionally, many school districts offer pension plans or 401(k) matching programs, providing long-term financial security. These benefits are particularly valuable for educators who plan to remain in the profession for an extended period, as they contribute to a stable and predictable retirement.
Paid Time Off and Work-Life Balance
Another significant benefit of teaching is the generous amount of paid time off, including summer breaks, holidays, and professional development days. This time allows teachers to recharge, pursue additional certifications, or even take on part-time work to supplement their income. For many educators, this work-life balance is a key factor in their decision to remain in the profession, even if their base salary may not be as high as in other fields.
Is Teaching a Lucrative Career Choice?
Many aspiring educators wonder whether teaching is a lucrative career choice, especially when considering how much teachers get paid. While teaching may not be the highest-paying profession, it offers unique rewards that extend beyond financial compensation. The sense of fulfillment that comes from shaping young minds and making a difference in students' lives is often cited as one of the most significant benefits of the profession.
That said, teaching can be financially viable for those who strategically navigate their careers. By pursuing advanced degrees, specializing in high-demand subjects, or taking on leadership roles, educators can significantly increase their earning potential. Additionally, the stability and job security that come with teaching make it an attractive option for many individuals, particularly in regions with strong union representation and favorable labor laws.
Ultimately, whether teaching is considered lucrative depends on individual priorities and circumstances. For those who value job satisfaction, work-life balance, and the opportunity to make a meaningful impact, teaching can be a highly rewarding career choice. However, it's essential to weigh these intangible benefits against the financial realities of the profession to make an informed decision.
How Can Teachers Increase Their Earning Potential?
While the base salary for teachers is often determined by external factors like location and experience, there are several proactive steps educators can take to increase their earning potential. By investing in their professional development and exploring additional opportunities, teachers can enhance their financial prospects while also advancing their careers.
Pursuing Advanced Degrees and Certifications
One of the most effective ways for teachers to boost their income is by pursuing advanced degrees or specialized certifications. Many school districts offer salary increases for educators who hold master's degrees or higher, recognizing the added value these qualifications bring to the classroom. Additionally, certifications in areas like special education, bilingual education, or technology integration can make teachers more competitive in the job market and lead to higher pay.
Exploring Part-Time Opportunities
Teachers can also supplement their income by taking on part-time work during school breaks or after hours. Tutoring, freelance writing, or online teaching are popular options that allow educators to leverage their expertise while earning extra money. These opportunities not only provide financial benefits but also help teachers expand their skill sets and stay engaged with their profession year-round.
What Role Do Policies Play in Teacher Compensation?
Policies at the local, state, and federal levels play a significant role in determining how much teachers get paid. Funding allocations, union negotiations, and legislative decisions all influence teacher salaries and benefits. For example, states with strong teachers' unions often have higher average salaries and better working conditions, as these organizations advocate for fair compensation and improved resources.
At the federal level, policies like Title I funding aim to support schools in low-income areas, which can indirectly impact teacher pay. However, disparities persist, particularly in regions where education is not prioritized in budgetary decisions. Advocacy and policy reform are essential for addressing these inequities and ensuring that all teachers receive fair and competitive compensation.
Frequently Asked Questions About Teacher Pay
What is the average salary for teachers in the United States?
The average salary for teachers in the U.S. varies by state but typically ranges from $45,000 to $70,000 annually. Factors such as experience, location, and subject matter influence these figures.
Do teachers receive raises over time?
Yes, most school districts have structured pay scales that provide annual raises based on experience and additional qualifications, such as advanced degrees or certifications.
How do benefits impact overall teacher compensation?
Benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off significantly enhance teacher compensation, often making teaching a more financially viable career choice.
In conclusion, understanding how much teachers get paid requires a nuanced examination of various factors, including geography, experience, and policy decisions. While challenges remain, there are opportunities for educators to increase their earning potential and advocate for fair compensation. By addressing these issues, we can ensure that teachers are valued and supported in their critical role of shaping the future.
For more information on teacher salaries and compensation, you can visit NEA.org, the official website of the National Education Association.